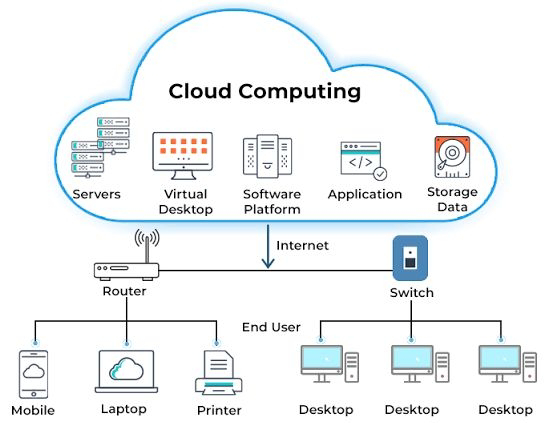
- In Cloud Computing model, the computing resources - be it a server hardware, storage, network, or application software - are available from the cloud vendor or provider's site/premises
- Resources available on the cloud can be accessed over the Internet from any remote location and by any local computing device.
- In addition, the usage or accessibility is to cost only to the level of usage to the customers based on their needs and demands, also known as the pay-as-you-go or pay-as-per-use model.
- All the resources available on the cloud are considered as services that can be availed on demand.
- One such service available on the cloud is the storage service. With the help of this service, we can store our family photographs, our favorite songs, and even movies on the cloud.
- Flickr is an example for storage service on the cloud through which we can store our images and photos, as well as share them with others
- Some of the advantages of using Flickr for storing our photos online are as follows:
- Flickr allows us to easily access our images no matter where we are or what type of device we are using
- Flickr lets us share the images
- Flickr provides backup for our files. By uploading the images to Flickr, we are creating backup on the web
Cloud Computing is a Platform:
- The basic meaning of the term platform is that it is the base or ground that provides the support for applications to exist and run on a hardware.
- For example, Microsoft Windows is a platform on which application software can be installed and run for the user to interact.
- The term platform refers not only operating system, but also many more in computer science:
- Java is a platform even though it is not an operating system. It provides the environment on which developers can develop and run applications of various kind using Java.
- Similarly, the World Wide Web (WWW) can be considered as the operating system (or platform) for all our Internet-based applications.
- In cloud computing model, WWW is a platform on which software such as Office 2.0, which was originally available on desktop computers, is now available on the web.
- Word processors like Buzzword and office suites like Google Docs are now available in the cloud as their desktop counter-parts.
Essential Characteristics of Cloud Computing:
- As per the definition of NIST, cloud model is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.
- Here is the description of those essential characteristics of Cloud Computing:
1. On-demand self-service: Consumers have the ability to independently and automatically provision computing resources—such as server time and network storage—without the need for direct human intervention with the service provider.
- This capability exemplifies the on-demand nature and elasticity of cloud services.
- Examples of resources available on the cloud include storage, processing, memory, and network bandwidth.
- This approach ensures broad compatibility and interoperability among heterogeneous platforms, supporting varied client environments
3. Elastic resource pooling: The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multitenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand.
- There is a sense of location independence in accessing the cloud
- The customer generally has no control or knowledge over the exact location of the provided resources but may be able to specify the location at a higher level of abstraction (e.g., country, state, or data center).
- To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be purchased in any quantity at any time.
5. Measured service: Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts).
- Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported providing transparency for both the provider and consumer of the utilized service.